
I am a last-year PhD student in PolyU NLP Group at The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, fortunately advised by Prof. Maggie, Wenjie Li.
Before that, I received my MSc and BMgt degrees from Huazhong University of Science and Technology.
Recently, I am interested in LLM-based reasoning and Medical AI. The specific topics include:
- Math Reasoning—subtle errors in reasoning and optimization strategies with jumping-start initialization;
- LLM Evaluation—robust multi-faceted evaluation and diverse test-scaling approaches;
- Clinician-like Medical Dialogue Systems—structured clinical communication, comprehensive differential diagnosis, and prototypical clinical reasoning processes;
🎙️ An invited talk I gave at Stanford MedAI is available on Youtube.
🔥 I am available on the job market and actively looking for industry opportunities!
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
http://".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "News
 NeurIPS 2025.
NeurIPS 2025. npj Artificial Intelligence.
npj Artificial Intelligence. ACL 2025.
ACL 2025. ICLR 2025.
ICLR 2025. Stanford MedAI, and will give a talk about medical dialogue systems on May 20th (YouTube).
Stanford MedAI, and will give a talk about medical dialogue systems on May 20th (YouTube). ACL 2024 Findings.
ACL 2024 Findings. ACL 2023 Main proceedings and Findings.
ACL 2023 Main proceedings and Findings.Selected Publications (View all)
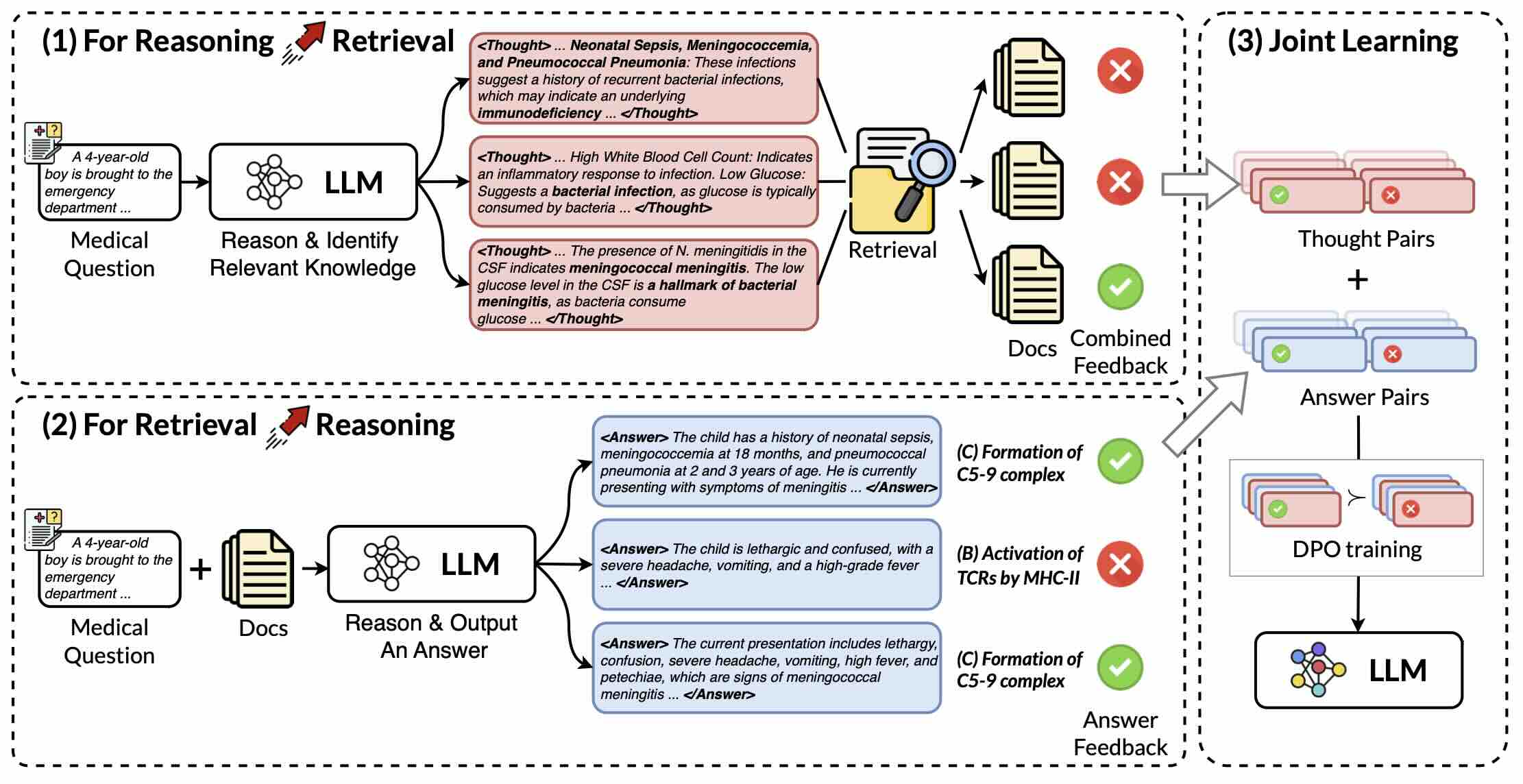
RAR^2: Retrieval-Augmented Medical Reasoning via Thought-Driven Retrieval
Kaishuai Xu, Wenjun Hou*, Yi Cheng*, Wenjie Li (* equal contribution)
EMNLP 2025 Findings Findings
In this work, we propose RAR^2, a joint learning framework that improves both Reasoning-Augmented Retrieval and Retrieval-Augmented Reasoning. Moreover, we design two test-time scaling strategies to explore the boundaries of our framework.
RAR^2: Retrieval-Augmented Medical Reasoning via Thought-Driven Retrieval
Kaishuai Xu, Wenjun Hou*, Yi Cheng*, Wenjie Li (* equal contribution)
EMNLP 2025 Findings Findings
In this work, we propose RAR^2, a joint learning framework that improves both Reasoning-Augmented Retrieval and Retrieval-Augmented Reasoning. Moreover, we design two test-time scaling strategies to explore the boundaries of our framework.
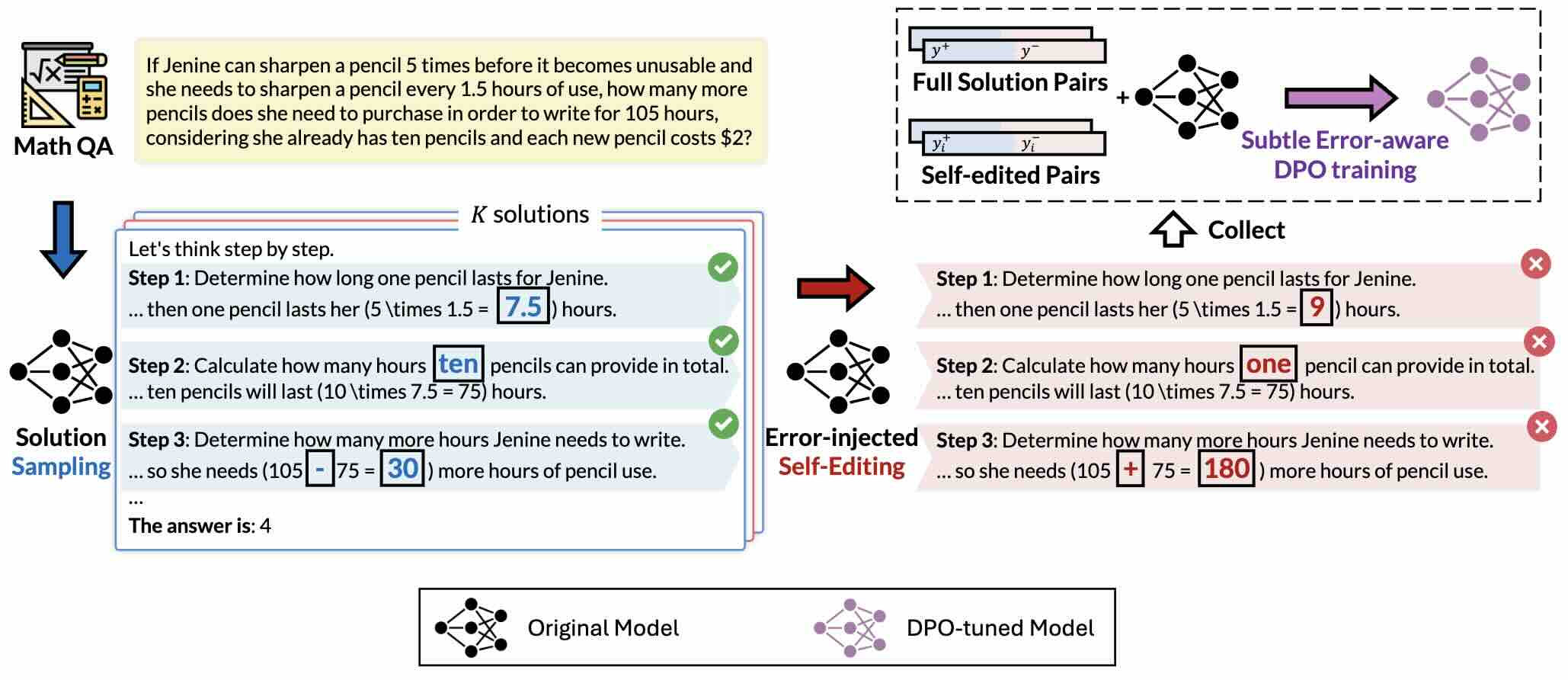
Subtle Errors in Reasoning: Preference Learning via Error-injected Self-editing
Kaishuai Xu, Tiezheng Yu, Wenjun Hou, Yi Cheng, Chak Tou Leong, Liangyou Li, Xin Jiang, Lifeng Shang, Qun Liu, Wenjie Li
ACL 2025 Main Conference
In this work, we propose a novel preference learning framework called eRror-Injected Self-Editing (RISE), which injects predefined subtle errors into pivotal tokens in reasoning or computation steps to construct hard pairs for error mitigation. Compared with other preference learning methods, RISE further refines the training objective without requiring fine-grained sampling or preference annotation.
Subtle Errors in Reasoning: Preference Learning via Error-injected Self-editing
Kaishuai Xu, Tiezheng Yu, Wenjun Hou, Yi Cheng, Chak Tou Leong, Liangyou Li, Xin Jiang, Lifeng Shang, Qun Liu, Wenjie Li
ACL 2025 Main Conference
In this work, we propose a novel preference learning framework called eRror-Injected Self-Editing (RISE), which injects predefined subtle errors into pivotal tokens in reasoning or computation steps to construct hard pairs for error mitigation. Compared with other preference learning methods, RISE further refines the training objective without requiring fine-grained sampling or preference annotation.
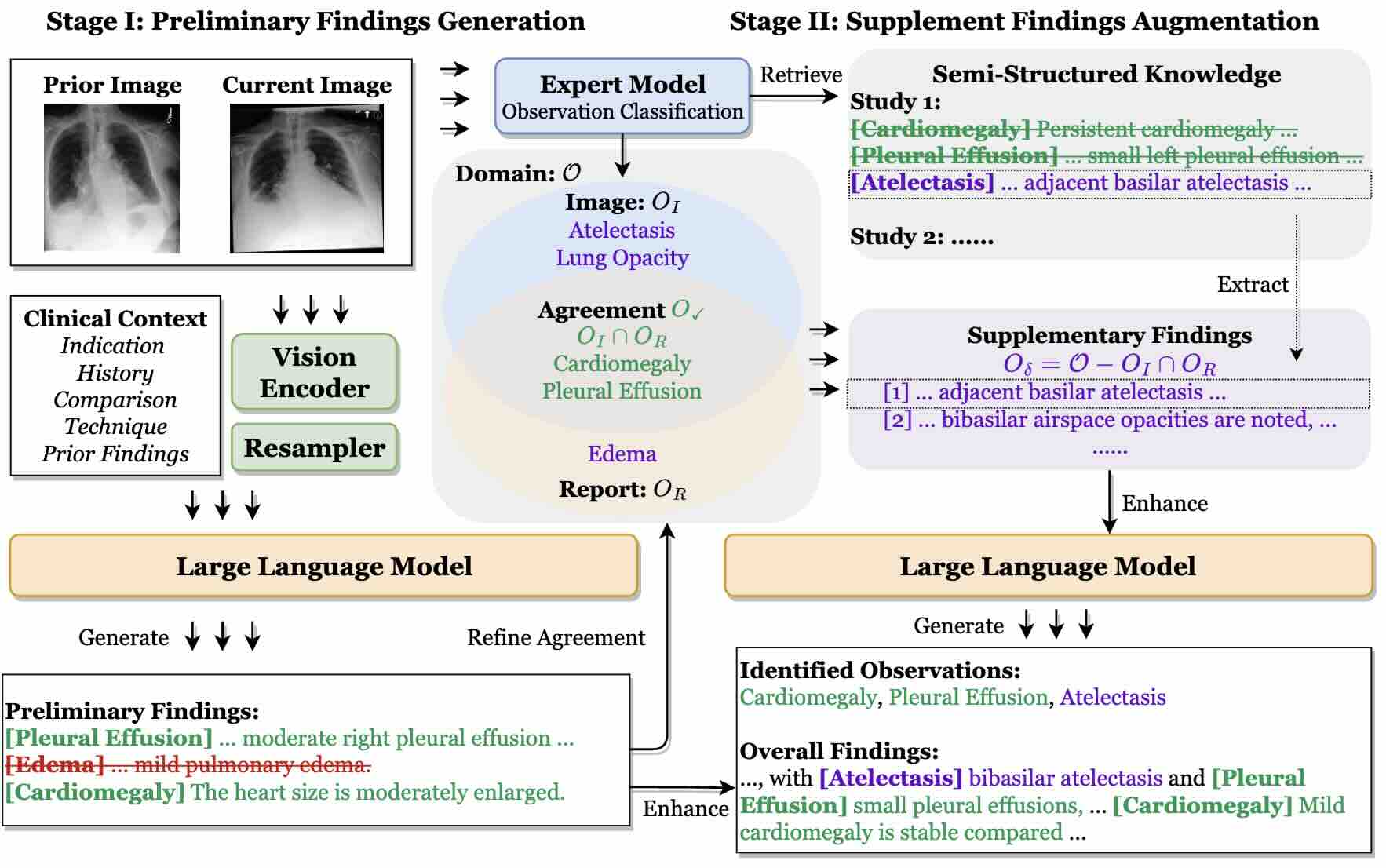
RADAR: Enhancing Radiology Report Generation with Supplementary Knowledge Injection
Wenjun Hou, Yi Cheng*, Kaishuai Xu*, Heng Li, Yan Hu, Wenjie Li, Jiang Liu (* equal contribution)
ACL 2025 Main Conference
We propose Radar, a framework for enhancing radiology report generation with supplementary knowledge injection. Radar improves report generation by systematically leveraging both the internal knowledge of an LLM and externally retrieved information.
RADAR: Enhancing Radiology Report Generation with Supplementary Knowledge Injection
Wenjun Hou, Yi Cheng*, Kaishuai Xu*, Heng Li, Yan Hu, Wenjie Li, Jiang Liu (* equal contribution)
ACL 2025 Main Conference
We propose Radar, a framework for enhancing radiology report generation with supplementary knowledge injection. Radar improves report generation by systematically leveraging both the internal knowledge of an LLM and externally retrieved information.
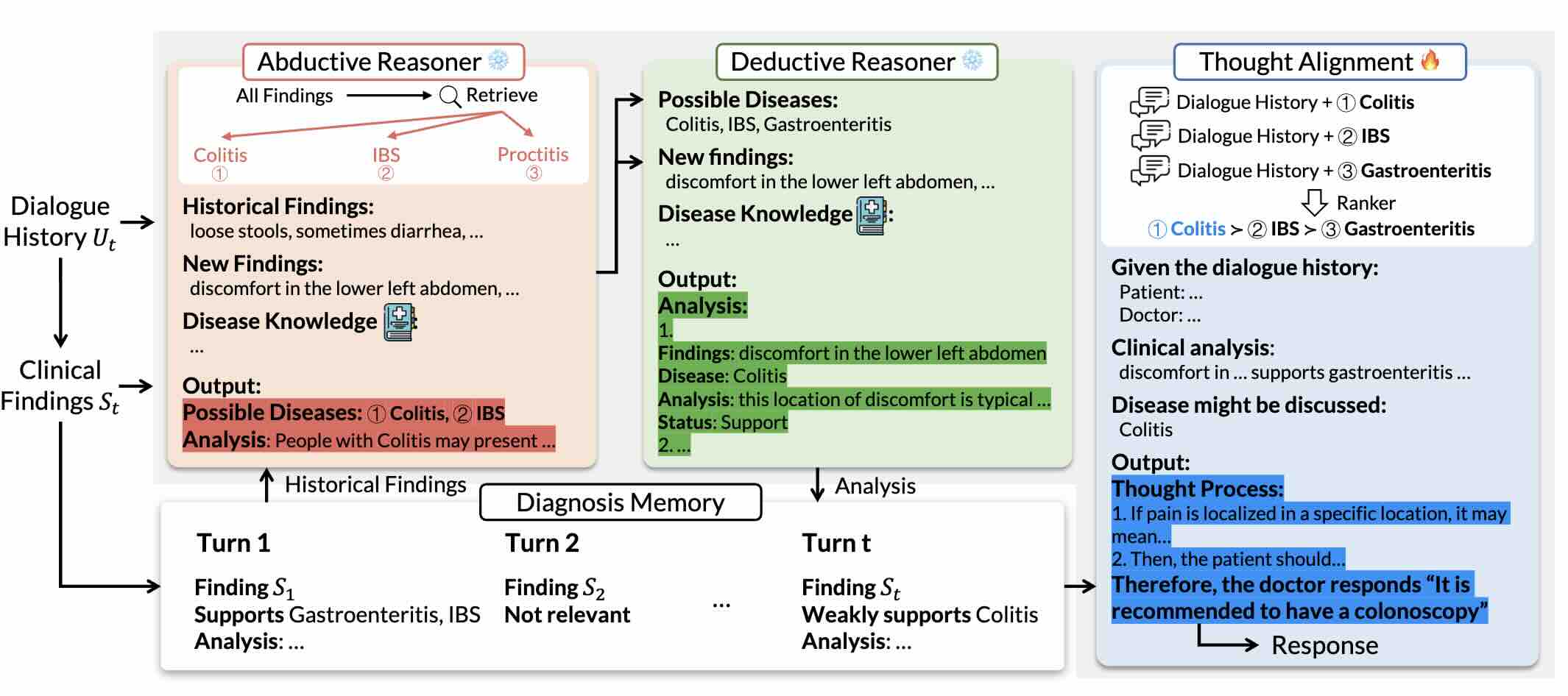
Reasoning Like a Doctor: Improving Medical Dialogue Systems via Diagnostic Reasoning Process Alignment
Kaishuai Xu, Yi Cheng*, Wenjun Hou*, Qiaoyu Tan, Wenjie Li (* equal contribution)
ACL 2024 Findings Findings
We propose a novel framework, Emulation, designed to generate an appropriate response that relies on abductive and deductive diagnostic reasoning analyses and aligns with clinician preferences through thought process modeling. Experimental results on two datasets confirm the efficacy of Emulation. Crucially, our framework furnishes clear explanations for the generated responses, enhancing its transparency in medical consultations.
Reasoning Like a Doctor: Improving Medical Dialogue Systems via Diagnostic Reasoning Process Alignment
Kaishuai Xu, Yi Cheng*, Wenjun Hou*, Qiaoyu Tan, Wenjie Li (* equal contribution)
ACL 2024 Findings Findings
We propose a novel framework, Emulation, designed to generate an appropriate response that relies on abductive and deductive diagnostic reasoning analyses and aligns with clinician preferences through thought process modeling. Experimental results on two datasets confirm the efficacy of Emulation. Crucially, our framework furnishes clear explanations for the generated responses, enhancing its transparency in medical consultations.
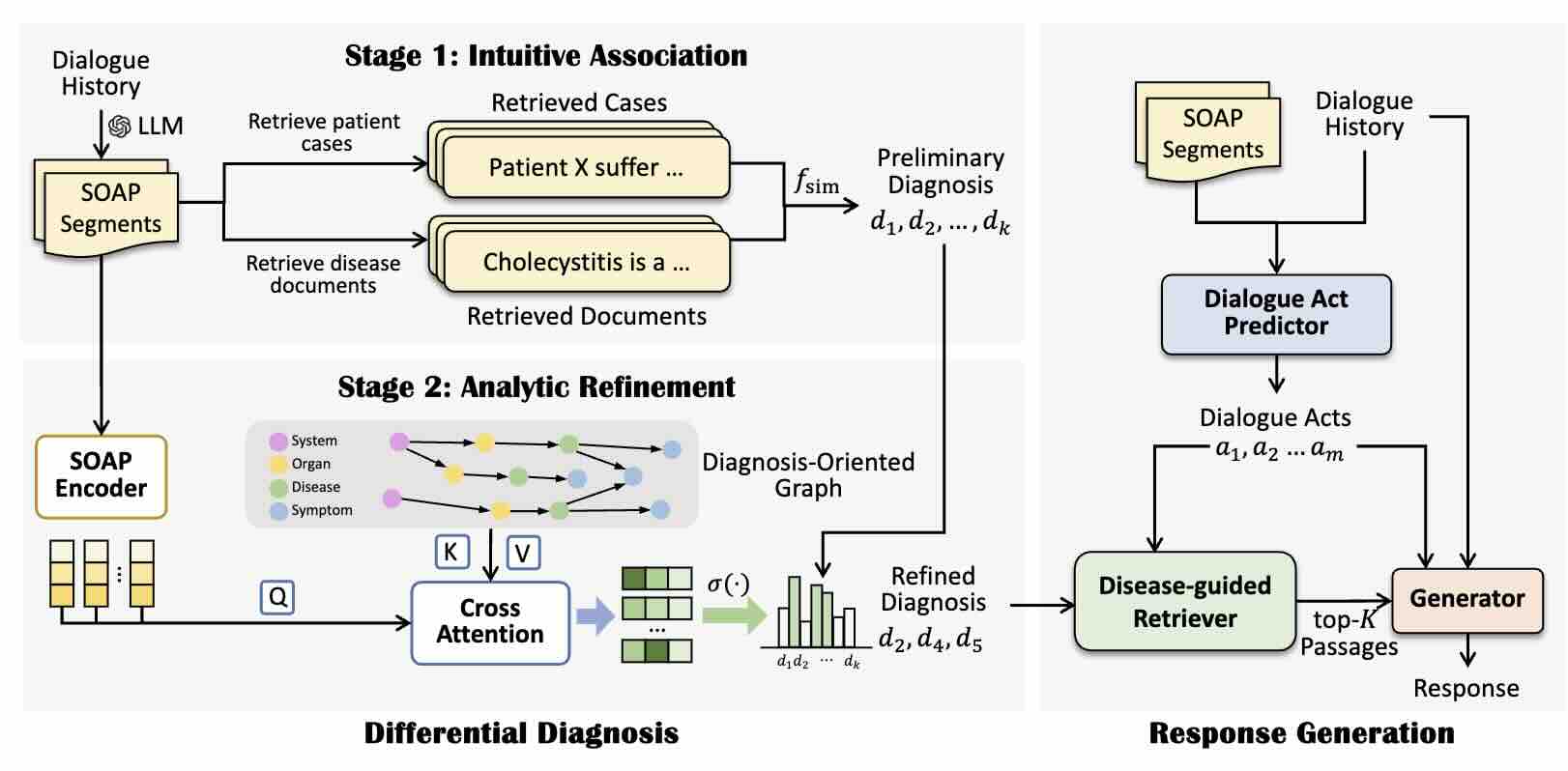
Medical Dialogue Generation via Intuitive-then-Analytical Differential Diagnosis
Kaishuai Xu, Wenjun Hou, Yi Cheng, Jian Wang, Wenjie Li
arXiv preprint 2024 Preprint
We propose a medical dialogue generation framework with the Intuitive-then-Analytic Differential Diagnosis (IADDx). Our method starts with a differential diagnosis via retrieval-based intuitive association and subsequently refines it through a graph-enhanced analytic procedure. The resulting differential diagnosis is then used to retrieve medical knowledge and guide response generation.
Medical Dialogue Generation via Intuitive-then-Analytical Differential Diagnosis
Kaishuai Xu, Wenjun Hou, Yi Cheng, Jian Wang, Wenjie Li
arXiv preprint 2024 Preprint
We propose a medical dialogue generation framework with the Intuitive-then-Analytic Differential Diagnosis (IADDx). Our method starts with a differential diagnosis via retrieval-based intuitive association and subsequently refines it through a graph-enhanced analytic procedure. The resulting differential diagnosis is then used to retrieve medical knowledge and guide response generation.
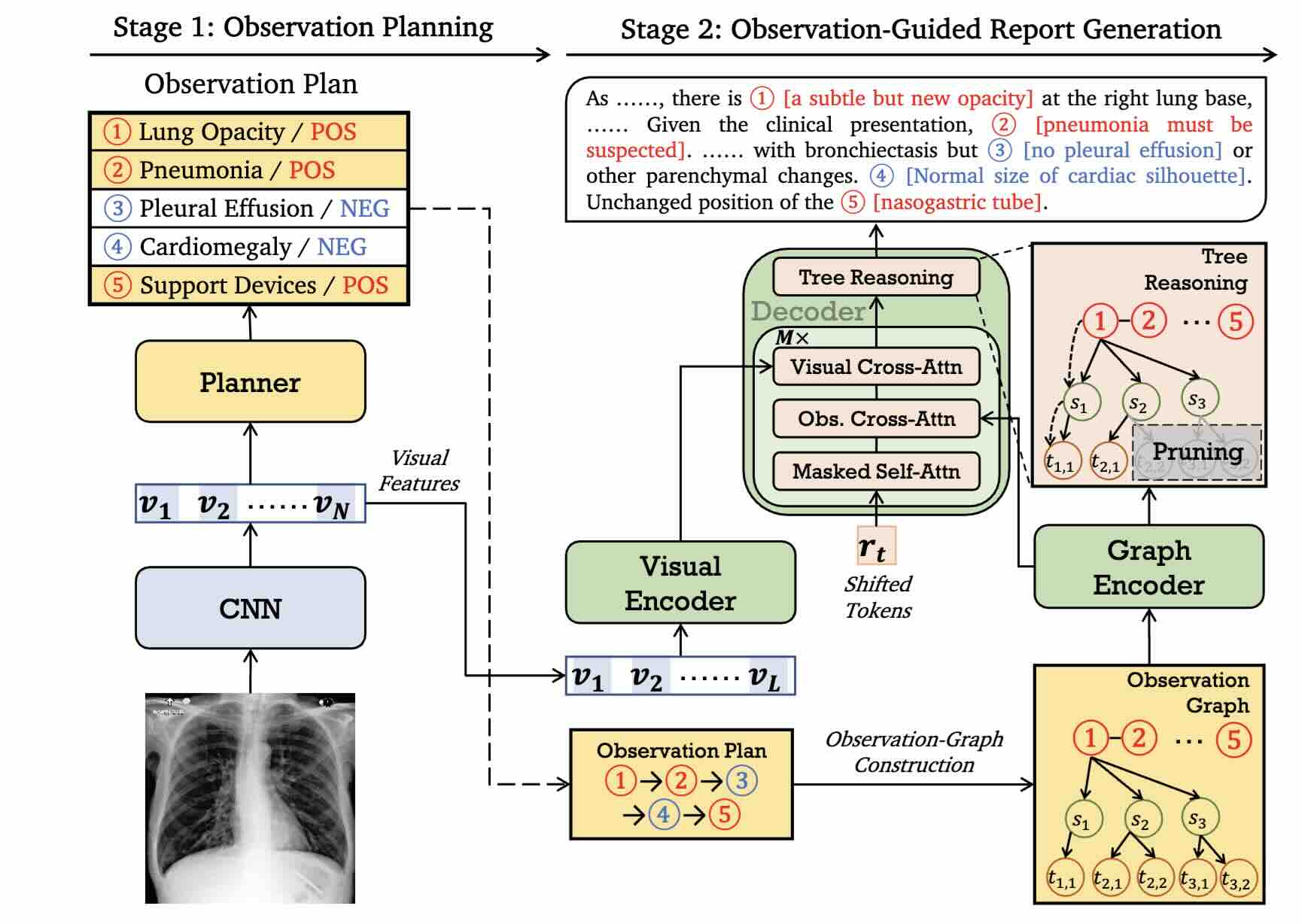
ORGAN: Observation-Guided Radiology Report Generation via Tree Reasoning
Wenjun Hou, Kaishuai Xu*, Yi Cheng*, Wenjie Li, Jiang Liu (* equal contribution)
ACL 2023 Main Proceedings
In this paper, we propose an Observation-guided radiology Report Generation framework (ORGan). It first produces an observation plan and then feeds both the plan and radiographs for report generation, where an observation graph and a tree reasoning mechanism are adopted to precisely enrich the plan information by capturing the multi-formats of each observation. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods regarding text quality and clinical efficacy.
ORGAN: Observation-Guided Radiology Report Generation via Tree Reasoning
Wenjun Hou, Kaishuai Xu*, Yi Cheng*, Wenjie Li, Jiang Liu (* equal contribution)
ACL 2023 Main Proceedings
In this paper, we propose an Observation-guided radiology Report Generation framework (ORGan). It first produces an observation plan and then feeds both the plan and radiographs for report generation, where an observation graph and a tree reasoning mechanism are adopted to precisely enrich the plan information by capturing the multi-formats of each observation. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods regarding text quality and clinical efficacy.
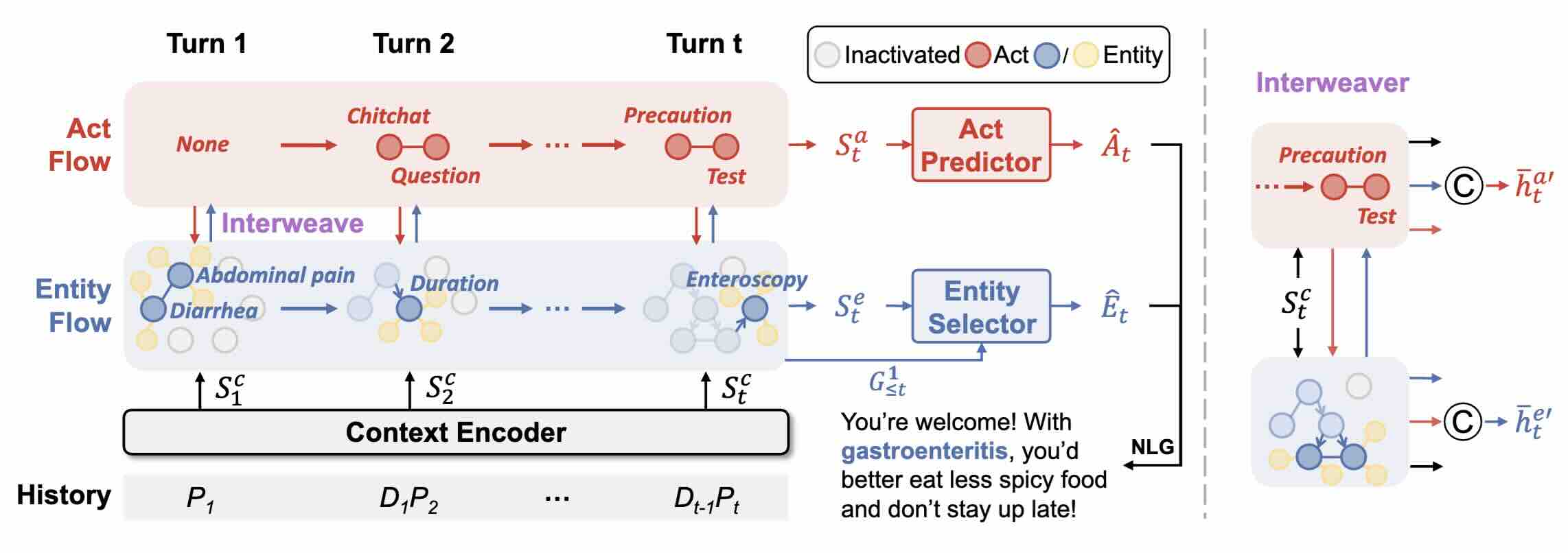
Medical Dialogue Generation via Dual Flow Modeling
Kaishuai Xu, Wenjun Hou*, Yi Cheng*, Jian Wang, Wenjie Li (* equal contribution)
ACL 2023 Findings Findings
We propose a Dual Flow enhanced Medical (DFMed) dialogue generation framework. It extracts the medical entities and dialogue acts used in the dialogue history and models their transitions with an entity-centric graph flow and a sequential act flow, respectively. We employ two sequential models to encode them and devise an interweaving component to enhance their interactions. Experiments on two datasets demonstrate that our method exceeds baselines in both automatic and manual evaluations.
Medical Dialogue Generation via Dual Flow Modeling
Kaishuai Xu, Wenjun Hou*, Yi Cheng*, Jian Wang, Wenjie Li (* equal contribution)
ACL 2023 Findings Findings
We propose a Dual Flow enhanced Medical (DFMed) dialogue generation framework. It extracts the medical entities and dialogue acts used in the dialogue history and models their transitions with an entity-centric graph flow and a sequential act flow, respectively. We employ two sequential models to encode them and devise an interweaving component to enhance their interactions. Experiments on two datasets demonstrate that our method exceeds baselines in both automatic and manual evaluations.